The weekly agenda_12.06.2020
Three phases of investing for the post-COVID-19 economy will fall into three overlapping periods: preservation, consolidation and innovation. The preservation is the period where uncertainty is so high that the best thing for both investors and governments to focus on funding and balance sheet repair. More importantly, business problems will have changed in a profoundly substantive way, and increasing request for new solutions will be high. From an investing standpoint, the key in navigating these phases will be to distinguish between competitive advantages that are sustainable and those that are a matter of circumstance. Supposedly, the specialization is eliminating the vertical integration towards more flexible business models. As the COVID-19 experience has shown how vulnerable vertically integrated firms were to any internal disruptions in non-core functions. At the same time, more flattering structures found it easier moving between vendors and technologies as they have been better adapted to changing circumstances.
The trickiest aspect for investors is a fairly stark difference between the competitive dynamics during the consolidation and innovation phases. We are coming to a period of intense consolidation and clusterization of market winners, followed by a massive thrive of new entrants from the small entities, structured for cost-effective resiliency. It has been quickly leading to an ongoing cycle of consolidation, regions specialization, skills development through an improvement of the local educational system. Successful industry players are typically applied for advanced analytics. They are accurately predicting their sub-sectors manufacturers whose supply system can increase by building stronger relationships while simultaneously helping small business to optimize their investment return.
The converged effort is required to optimize investment within digital channels and across the acquisition funnel to align with investors’ shifting preferences and needs. Given the analytical nature of digital marketing, required skill sets differ vastly from “old-fashioned” marketing. Its teams more closely resemble Math Men, doing digital traffic generation, existing customer engagement, and conversion. Leading digital companies leverage multiple marketing channels and customize strategies to customer segments, in combination with a sharp focus on developing truly exceptional customer journeys.
The World Bank is expecting the global economy to shrink by 5.2% this year, in the deepest recession since World War Two. It is said that the US economy is expected to contract by 6.1% and the Euro area to shrink by 9.1%. Regulatory reset is the idea that we will see a large change in the legal and regulatory framework that will create many new business opportunities. Once the rules are set, we tend to see both cheaper responses and the desire of large firms to exit riskier activities and drive a wave of innovations and new entrants. In the second phase, the regulation shift will mainly be about the lack of innovative competition, the economic imbalances that will accompany that increase in technology shortage. The kick-off a regulatory wave will be supporting the new entry, being a genuine policymakers matter.
Although the total growth in the unemployment rate can be considered as influential, the economy shows the signs of slow revival. For instance, according to the official statistic information, the unemployment rate in the USA has reached 13% these days. According to “the Times”, British Petroleum cut about 15 per cent of its workforce in response to the global slowdown and the effect it has had in pushing the oil price sharply lower. As a result, global unemployment will affect an increase of public tension.
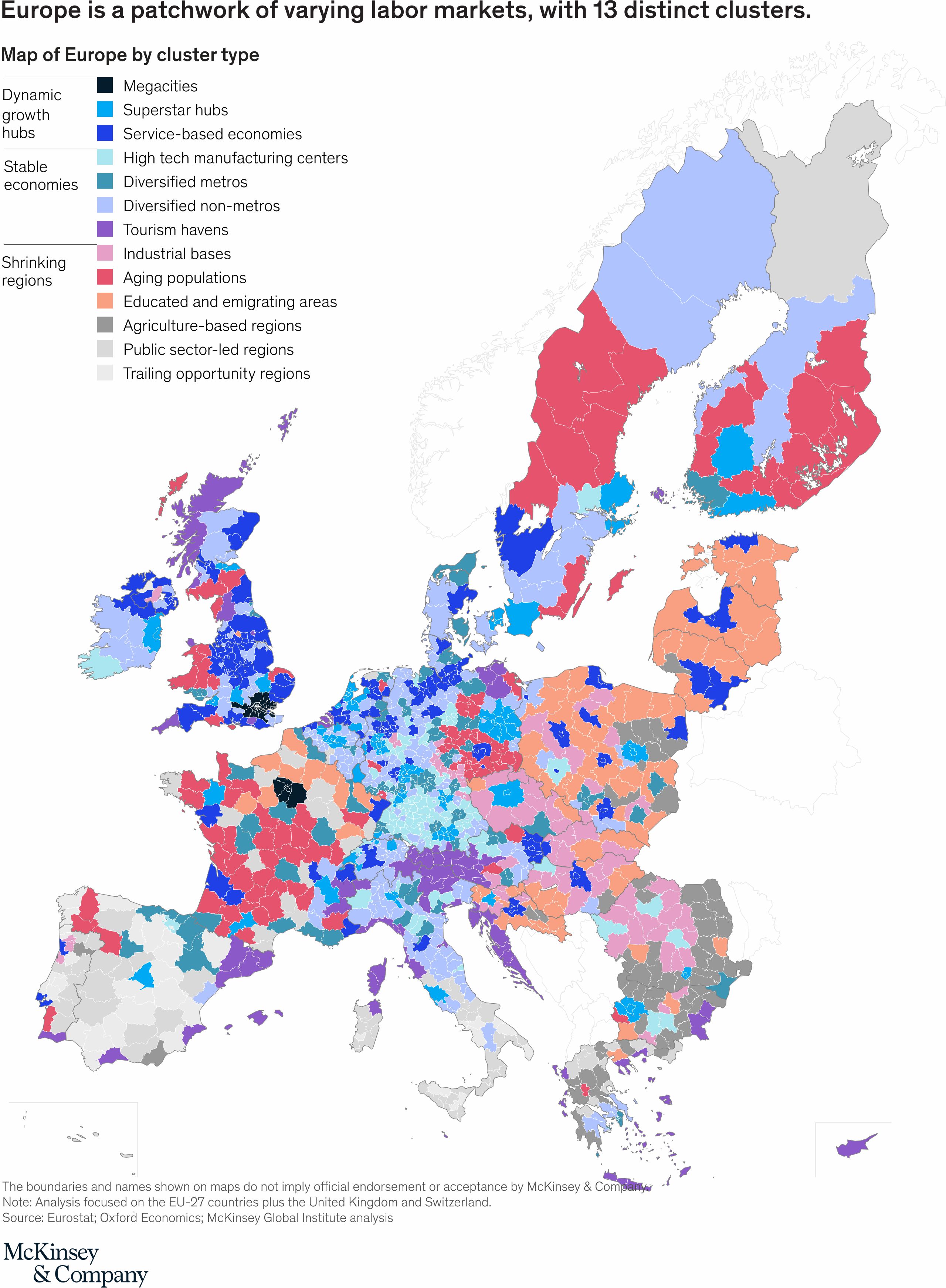
Shrinking labour markets need targeted economic development strategies For policymakers, the prospect of even more polarized job, GDP, and population growth carries the risk of exacerbating social tensions and inequality. Occupational and geographic mismatches are likely to emerge as a major challenge over the next decade (Exhibit 1). Up to 21 million may have to leave declining occupations. Thereby it is found that 78 per cent of people who moved into four highly sought-after occupations—software engineer, recruiter, talent acquisition specialist, and digital marketing specialist— came from extensive knowledge occupations. In megacities and superstar hubs, estimates suggest that existing residents can fill less than 60 per cent of expected job growth. Filling the remaining skills shortage in these dynamic growth hubs will require 4.4 per cent of the ex-pats engaging. Our model suggests possible net growth rates of 15 per cent in the two megacities and 9 per cent for the superstar hubs in the midpoint automation scenario. Findings suggest that automation and occupational and skill shifts that accompany would accelerate the concentration of potential net job growth. The same megacities and thriving clusters hubs that contributed 35 per cent of the job growth in the past decade could capture more than 50 per cent by 2030.
The crucial meeting in Pskov held by Mikhail Vedernikov and anchor Moglino SEZ tenant, represented by its shareholder Mikhail Sutyaginskiy, took place along with the discussion of the experienced challenges and clear prospects. It has been highlighted—what worked, what didn’t under hardship. The agenda was about Titan Polymer project development, localized at the Molino 2- section. It has also been discussed that the regional Small business will benefit by extension within the giant cluster, as well as skills development, urban infrastructure development in general. The railway infrastructure involves difficult trade-offs related to funding support. Thus, Moglino SEZ should decide whether and how to invest public money or to attract private funds. The main point coming from this event is Small business and education providers opportunities to meet the growing demand for sub-sectors manufacturing and upskilling.
We need to create more training and career pathways connected with the regional clusters. Creating partnerships between educators and employers could help in the design of career-relevant curricula. Employers will be natural providers of training opportunities for many, and policymakers can consider providing incentives to companies that invest in workforce development. Access to jobs in dynamic growth hubs needs to be expanded to fulfill their growth potential.
Moglino SEZ and biological faculty of Pskov State University and Moscow State University is going to converge efforts to design and blueprint relevant curricula and research centre, establish prospect, aimed to boost innovative manufactories.

